Endodontics is the field of dentistry which deals with causes, diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of diseases of the dental pulp as well as their consequences. The scientific field of Endodontics deals specifically with the problems of the dental roots. The most commonly known Endodontic procedure is the Root Canal Treatment.
Root Canal Treatment:
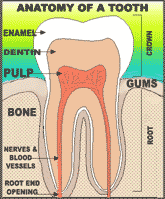
“Endo” is the Greek word for “inside” and “odont” is Greek for “tooth.” Endodontic treatment treats the inside of the tooth. To understand endodontic treatment, it helps to know something about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white
enamel and a hard layer called the
dentin, is a soft tissue called the
pulp. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue and creates the surrounding hard tissues of the tooth during development. The pulp extends from the
crown of the tooth to the tip of the
roots where it connects to the tissues surrounding the root. The pulp is important during a tooth’s growth and development. However, once a tooth is fully mature it can survive without the pulp, because the tooth continues to be nourished by the tissues surrounding it.
Endodontic treatment is necessary when the pulp, the soft tissue inside the root canal, becomes inflamed or infected. The inflammation or infection can have a variety of causes: deep decay, repeated dental procedures on the tooth, or a crack or chip in the tooth. In addition, an injury to a tooth may cause pulp damage even if the tooth has no visible chips or cracks. If pulp inflammation or infection is left untreated, it can cause pain or lead to an abscess.
Signs to look for include pain, prolonged sensitivity to heat or cold, tenderness to touch and chewing, discoloration of the tooth, and swelling, drainage and tenderness in the lymph nodes as well as nearby bone and gingival tissues. Sometimes, however, there are no symptoms.
The endodontist removes the inflamed or infected pulp, carefully cleans and shapes the inside of the canal, a channel inside the root, then fills and seals the space. Afterwards, you will return to your dentist, who will place a crown or other restoration on the tooth to protect and restore it to full function. After restoration, the tooth continues to function like any other tooth.
Many endodontic procedures are performed to relieve the pain of toothaches caused by pulp inflammation or infection. With modern techniques and anesthetics, most patients report that they are comfortable during the procedure.
For the first few days after treatment, your tooth may feel sensitive, especially if there was pain or infection before the procedure. This discomfort can be relieved with over-the-counter or prescription medications. Follow your endodontist’s instructions carefully.
Your tooth may continue to feel slightly different from your other teeth for some time after your endodontic treatment is completed. However, if you have severe pain or pressure or pain that lasts more than a few days, call your endodontist.
You should not chew or bite on the treated tooth until you have had it restored by your dentist. The unrestored tooth is susceptible to fracture, so you should see your dentist for a full restoration as soon as possible. Otherwise, you need only practice good oral hygiene, including brushing, flossing, and regular checkups and cleanings. Most endodontically treated teeth last as long as other natural teeth. In a few cases, a tooth that has undergone endodontic treatment does not heal or the pain continues. Occasionally, the tooth may become painful or diseased months or even years after successful treatment. Often when this occurs, redoing the endodontic procedure can save the tooth.
New trauma, deep decay, or a loose, cracked or broken filling can cause new infection in your tooth. In some cases, the endodontist may discover additional very narrow or curved canals that could not be treated during the initial procedure.
Most teeth can be treated. Occasionally, a tooth can’t be saved because the root canals are not accessible, the root is severely fractured, the tooth doesn’t have adequate bone support, or the tooth cannot be restored. However, advances in endodontics are making it possible to save teeth that even a few years ago would have been lost. When endodontic treatment is not effective, endodontic surgery may be able to save the tooth.
The cost varies depending on how complex the problem is and which tooth is affected. Molars are more difficult to treat, the fee is usually more. Most dental insurance policies provide some coverage for endodontic treatment. Generally, endodontic treatment and restoration of the natural tooth are less expensive than the alternative of having the tooth extracted. An extracted tooth must be replaced with a bridge or implant to restore chewing function and prevent adjacent teeth from shifting. These procedures tend to cost more than endodontic treatment and appropriate restoration. With root canal treatment you save your natural teeth and money.
Root Canal Retreatment:
Occasionally, a tooth which has already had root canal treatment may require treatment again, or root canal retreatment.
As occasionally happens with any dental or medical procedure, a tooth may not heal as expected after initial treatment for a variety of reasons:
- Narrow or curved canals were not treated during the initial procedure.
- Complicated canal anatomy went undetected in the first procedure.
- The placement of the crown or other restoration was delayed following the endodontic treatment.
- The restoration did not prevent salivary contamination to the inside of the tooth.
In other cases, a new problem can jeopardize a tooth that was successfully treated. For example:
- New decay can expose the root canal filling material to bacteria, causing a new infection in the tooth.
- A loose, cracked or broken crown or filling can expose the tooth to new infection.
- A tooth sustains a fracture.
First, the endodontist will discuss your treatment options. If you and your endodontist choose retreatment, the endodontist will reopen your tooth to gain access to the root canal filling material. In many cases, complex restorative materials—crown, post and core material—must be disassembled and removed to permit access to the root canals.
After removing the canal filling, the endodontist can clean the canals and carefully examine the inside of your tooth using magnification and illumination, searching for any additional canals or unusual anatomy that requires treatment.
After cleaning the canals, the endodontist will fill and seal the canals and place a temporary filling in the tooth. If the canals are unusually narrow or blocked, your endodontist may recommend endodontic surgery. This surgery involves making an incision to allow the other end of the root to be sealed. After your endodontist completes retreatment, you will need to return to your dentist as soon as possible to have a new crown or other restoration placed on the tooth to protect and restore it to its full function.
Whenever possible, it is best to save your natural tooth. Retreated teeth can function well for years, even for a lifetime.
Advances in technology are constantly changing the way root canal treatment is performed, so your endodontist may use new techniques that were not available when you had your first procedure. Your endodontist may be able to resolve your problem with retreatment.
As with any dental or medical procedure, there are no guarantees. Your endodontist will discuss your options and the chances of success before beginning retreatment.
The cost varies depending on how complicated the procedure will be. The procedure will probably be more complex than your first root canal treatment, because your restoration and filling material may need to be removed to accomplish the new procedure. In addition, your endodontist may need to spend extra time searching for unusual canal anatomy. Therefore, you can generally expect retreatment to cost more than the initial endodontic treatment.
While dental insurance may cover part or all of the cost for retreatment, some policies limit coverage to a single procedure on a tooth in a given period of time. Check with your employer or insurance company prior to retreatment to be sure of your coverage.
If nonsurgical retreatment is not an option, then endodontic surgery should be considered. This surgery involves making an incision to allow access to the tip of the root. Endodontic surgery may also be recommended in conjunction with retreatment or as an alternative. Your endodontist will discuss your options and recommend appropriate treatment.
The only other alternative is extraction of the tooth. The extracted tooth must then be replaced with an implant, bridge or removable partial denture to restore chewing function and to prevent adjacent teeth from shifting. Because these options require extensive surgery or dental procedures on adjacent healthy teeth, they can be far more costly and time consuming than retreatment and restoration of the natural tooth. No matter how effective tooth replacements are—nothing is as good as your own natural tooth. You’ve already made an investment in saving your tooth. The payoff for choosing retreatment could be a healthy, functioning natural tooth for many years to come.
Root Canal Surgery:
- Surgery can help save your tooth in a variety of situations.
- Surgery may be used in diagnosis. If you have persistent symptoms but no problems appear on your x-ray, your tooth may have a tiny fracture or canal that could not be detected during nonsurgical treatment. In such a case, surgery allows your endodontist to examine the entire root of your tooth, find the problem, and provide treatment.
- Sometimes calcium deposits make a canal too narrow for the instruments used in nonsurgical root canal treatment to reach the end of the root. If your tooth has this “calcification,” your endodontist may perform endodontic surgery to clean and seal the remainder of the canal.
- Usually, a tooth that has undergone a root canal can last the rest of your life and never need further endodontic treatment. However, in a few cases, a tooth may not heal or become infected. A tooth may become painful or diseased months or even years after successful treatment. If this is true for you, surgery may help save your tooth.
- Surgery may also be performed to treat damaged root surfaces or surrounding bone.
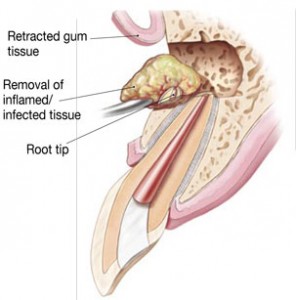
In this procedure, the endodontist opens the gum tissue near the tooth to see the underlying bone and to remove any inflamed or infected tissue. The very end of the root is also removed. A small filling may be placed in the root to seal the end of the root canal, and a few stitches or sutures are placed in the gingiva to help the tissue heal properly. Over a period of months, the bone heals around the end of the root.
Other surgeries endodontists might perform include dividing a tooth in half, repairing an injured root, or even removing one or more roots. Your endodontist will be happy to discuss the specific type of surgery your tooth requires. In certain cases, a procedure called intentional replantation may be performed. In this procedure, a tooth is extracted, treated with an endodontic procedure while it is out of the mouth, and then replaced in its socket. These procedures are designed to help you save your tooth.
Local anesthetics make the procedure comfortable. Of course, you may feel some discomfort or experience slight swelling while the incision heals. This is normal for any surgical procedure. Your endodontist will recommend appropriate pain medication to alleviate your discomfort. Your endodontist will give you specific postoperative instructions to follow. If you have questions after your procedure, or if you have pain that does not respond to medication, call your endodontist.
Often you can, but you should ask your endodontist before your appointment so that you can make transportation arrangements if necessary.
Most patients return to work or other routine activities the next day. Your endodontist will be happy to discuss your expected recovery time with you.
Each insurance plan is different. Check with your employer or insurance company prior to treatment.
Your dentist or endodontist is suggesting endodontic surgery because he or she believes it is the best option for saving your own natural tooth. Of course, there are no guarantees with any surgical procedure. Your endodontist will discuss your chances for success so that you can make an informed decision.
Often, the only alternative to surgery is extraction of the tooth. The extracted tooth must then be replaced with an implant, bridge, or removable partial denture to restore chewing function and to prevent adjacent teeth from shifting. Because these alternatives require surgery or dental procedures on adjacent healthy teeth, endodontic surgery is usually the most biologic and cost-effective option for maintaining your oral health. No matter how effective modern artificial tooth replacements are—and they can be very effective—nothing is as good as a natural tooth. You’ve already made an investment in saving your tooth. The pay-off for choosing endodontic surgery could be a healthy, functioning natural tooth for the rest of your life.
For more information, you could visit the website
AAE.org.
Cracked Teeth:
Cracked teeth show a variety of symptoms, including erratic pain when chewing, possibly with release of biting pressure, or pain when your tooth is exposed to temperature extremes. In many cases, the pain may come and go, and your dentist may have difficulty locating which tooth is causing the discomfort.
To understand why a cracked tooth hurts, it helps to know something about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is the inner soft tissue called the pulp. The loose pulp is a connective tissue that contains cells, blood vessels and nerves.
When the outer hard tissues of the tooth are cracked, chewing can cause movement of the pieces, and the pulp can become irritated. When biting pressure is released, the crack can close quickly, resulting in a momentary, sharp pain. Irritation of the dental pulp can be repeated many times by chewing. Eventually, the pulp will become damaged to the point that it can no longer heal itself. The tooth will not only hurt when chewing but may also become sensitive to temperature extremes. In time, a cracked tooth may begin to hurt all by itself. Extensive cracks can lead to infection of the pulp tissue, which can spread to the bone and gum tissue surrounding the tooth.
There are many different types of cracked teeth. The treatment and outcome for your tooth depends on the type, location, and extent of the crack.
Craze Lines
Craze lines are tiny cracks that affect only the outer enamel. These cracks are extremely common in adult teeth. Craze lines are very shallow, cause no pain, and are of no concern beyond appearances.
Fractured Cusp
When a cusp (the pointed part of the chewing surface) becomes weakened, a fracture sometimes results. The weakened cusp may break off by itself or may have to be removed by the dentist. When this happens, the pain will usually be relieved. A fractured cusp rarely damages the pulp, so root canal treatment is seldom needed. Your tooth will usually be restored with a full crown by your dentist.
Cracked Tooth
This crack extends from the chewing surface of the tooth vertically towards the root. A cracked tooth is
not completely separated into two distinct segments. Because of the position of the crack, damage to the pulp is common. Root canal treatment is frequently needed to treat the injured pulp. Your dentist will then restore your tooth with a crown to hold the pieces together and protect the cracked tooth. At times, the crack may extend below the gingival tissue line, requiring
tooth extraction. A nontreatable tooth is shown in the graphic above.
Early diagnosis is important. Even with high magnification and special lighting, it is sometimes difficult to determine the extent of a crack. A cracked tooth that is not treated will progressively worsen, eventually resulting in the loss of the tooth. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential in saving these teeth.
Split Tooth
A split tooth is often the result of the long term progression of a cracked tooth. The split tooth is identified by a crack with distinct segments that can be separated. A split tooth cannot be saved intact. The position and extent of the crack, however, will determine whether any portion of the tooth can be saved. In rare instances, endodontic treatment and a crown or other restoration by your dentist may be used to save a portion of the tooth.
Vertical Root Fracture
Vertical root fractures are cracks that begin in the root of the tooth and extend toward the chewing surface. They often show minimal signs and symptoms and may therefore go unnoticed for some time. Vertical root fractures are often discovered when the surrounding bone and gum become infected. Treatment may involve extraction of the tooth. However, endodontic surgery is sometimes appropriate if a portion of the tooth can be saved by removal of the fractured root.
Unlike a broken bone, the fracture in a cracked tooth will not heal. In spite of treatment, some cracks may continue to progress and separate, resulting in loss of the tooth. Placement of a crown on a cracked tooth provides maximum protection but does not guarantee success in all cases.
The treatment you receive for your cracked tooth is important because it will relieve pain and reduce the likelihood that the crack will worsen. Once treated, most cracked teeth continue to function and provide years of comfortable chewing. Talk to your endodontist about your particular diagnosis and treatment recommendations. S/he will advise you on how to keep your natural teeth and achieve optimum dental health.
While cracked teeth are not completely preventable, you can take some steps to make your teeth less susceptible to cracks.
- Don't chew on hard objects such as ice, unpopped popcorn kernels or pens.
- Don't clench or grind your teeth.
- If you clench or grind your teeth while you sleep, talk to your dentist about getting a retainer or other mouthguard to protect your teeth.
- Wear a mouthguard or protective mask when playing contact sports.
 “Endo” is the Greek word for “inside” and “odont” is Greek for “tooth.” Endodontic treatment treats the inside of the tooth. To understand endodontic treatment, it helps to know something about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is a soft tissue called the pulp. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue and creates the surrounding hard tissues of the tooth during development. The pulp extends from the crown of the tooth to the tip of the roots where it connects to the tissues surrounding the root. The pulp is important during a tooth’s growth and development. However, once a tooth is fully mature it can survive without the pulp, because the tooth continues to be nourished by the tissues surrounding it.
“Endo” is the Greek word for “inside” and “odont” is Greek for “tooth.” Endodontic treatment treats the inside of the tooth. To understand endodontic treatment, it helps to know something about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is a soft tissue called the pulp. The pulp contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue and creates the surrounding hard tissues of the tooth during development. The pulp extends from the crown of the tooth to the tip of the roots where it connects to the tissues surrounding the root. The pulp is important during a tooth’s growth and development. However, once a tooth is fully mature it can survive without the pulp, because the tooth continues to be nourished by the tissues surrounding it. Endodontic treatment can often be performed in one or two visits and involves the following steps:
Endodontic treatment can often be performed in one or two visits and involves the following steps:
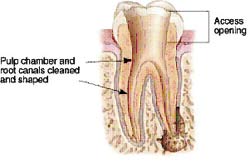 After the space is cleaned and shaped, the endodontist fills the root canals with a biocompatible material, usually a rubber-like material called “gutta-percha.” The gutta-percha is placed with an adhesive cement to ensure complete sealing of the root canals. In most cases, a temporary filling is placed to close the opening. The temporary filling will be removed by your dentist before the tooth is restored.
After the space is cleaned and shaped, the endodontist fills the root canals with a biocompatible material, usually a rubber-like material called “gutta-percha.” The gutta-percha is placed with an adhesive cement to ensure complete sealing of the root canals. In most cases, a temporary filling is placed to close the opening. The temporary filling will be removed by your dentist before the tooth is restored.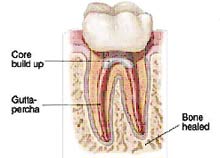 After the final visit with your endodontist, you must return to your dentist to have a crown or other restoration placed on the tooth to protect and restore it to full function. If the tooth lacks sufficient structure to hold the restoration in place, your dentist or endodontist may place a post inside the tooth. Ask your dentist or endodontist for more details about the specific restoration planned for your tooth.
After the final visit with your endodontist, you must return to your dentist to have a crown or other restoration placed on the tooth to protect and restore it to full function. If the tooth lacks sufficient structure to hold the restoration in place, your dentist or endodontist may place a post inside the tooth. Ask your dentist or endodontist for more details about the specific restoration planned for your tooth. In this procedure, the endodontist opens the gum tissue near the tooth to see the underlying bone and to remove any inflamed or infected tissue. The very end of the root is also removed. A small filling may be placed in the root to seal the end of the root canal, and a few stitches or sutures are placed in the gingiva to help the tissue heal properly. Over a period of months, the bone heals around the end of the root.
In this procedure, the endodontist opens the gum tissue near the tooth to see the underlying bone and to remove any inflamed or infected tissue. The very end of the root is also removed. A small filling may be placed in the root to seal the end of the root canal, and a few stitches or sutures are placed in the gingiva to help the tissue heal properly. Over a period of months, the bone heals around the end of the root.